Redoubt 1989/12
Start: 09:47:00 December 14, 1989 [1]
Stop: June 1990 [1]
Event Type: Explosive
Max VEI: 3 [2]
Description: From Miller and others (1998): "The most recent eruption at Redoubt began with a major phreatomagmatic, vent-clearing explosion at 9:47 am on December 14, 1989 (Brantley, 1990; EOS, 1990; Miller and Chouet, 1994) after less than 24 hours of intense precursory seismicity. Three more ash-rich explosions occurred the following day, December 15, with the last blast generating a pyroclastic flow down the Drift Glacier. The resulting debris flow contained entrained ice blocks as large as 10 m across and crested about 8 m above the river channel near the Drift River Oil Terminal, 35 km downstream (Waitt and others, 1994). A Boeing 747 enroute from Amsterdam that flew into the ash cloud several hours after the eruption experienced complete engine failure and narrowly avoided tragedy when the crew successfully restarted the engines and safely landed in Anchorage (Casadevall, 1994).
"These initial explosive events were just the first of 23 major explosive events between December 1989 and April 1990. Following the mid-December explosive phases, the crater vent emitted only minor ash and steam for the next 5-7 days. From December 22 to January 2, 1990, however, a large, over-steepened lava dome grew over the vent. At 5:48 pm on January 2, the first of two powerful explosions destroyed most of the dome and sent ash plumes to over 12 km. Massive block and ash avalanches down the Drift Glacier generated the largest debris flow of the eruption, completely covering the 2-km-wide valley floor and spilling into Cook Inlet. Flood waters entered the oil terminal, as much as 75 cm deep in some buildings, and caused a temporary halt in operations.
"Three eruptions occurred in the next two weeks during which time the vent remained open. The January 8 event occurred with no precursory warnings and the resulting ashfall on the Kenai Peninsula disrupted commerce and transportation. Open-vent eruptions on January 11 and 16 resulted in minor debris flows down the Drift River.
"After the January 16 eruption, another period of dome growth ensued through mid-February. This dome was smaller than the earlier dome but larger than succeeding domes (Miller, 1994). Early on February 15, the dome was destroyed in an explosive eruption that again sent a large debris flow down the Drift River and blanketed the lower Kenai Peninsula with ash. A pyroclastic flow and surge traveled down the canyon, across the piedmont lobe of Drift Glacier, and swept up the opposite valley wall 700 m topping the ridge (Gardner and others, 1994). Flow down the Drift River was largely diverted into a side drainage that carried flood waters close to oil storage tanks at the downstream oil terminal prompting reinforcement of the containment dikes surrounding the tank farm. A new dome began growing immediately following the eruption.
"On February 21, the new, but considerably smaller, dome was destroyed, marking the beginning of a new trend in eruptive behavior. Characteristically, small domes were emplaced and subsequently destroyed explosively or by gravitational collapse, resulting in debris avalanches down the now ice-free canyon leading down to the Drift River valley, and flooding down the Drift River. Ten such eruptions followed from February 24 to April 21 at 4 to 8 day intervals.
"Following the April 21 eruption, growth of the present lava dome began and continued through early June. During the next several months, seismic activity declined dramatically and only steam emissions and minor rock falls from the dome were recorded as the eruption came to an end.
"The 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt seriously affected the populace, commerce, and oil production throughout the Cook Inlet region and air traffic as far away as Texas. Total estimated economic costs are $160 million (Tuck and others, 1992), making this eruption of Redoubt the second most costly in U.S. history."
From Miller and Chouet (1994): "The eruption produced about 20 significant tephra deposits between December 14 and April 26 (Scott and McGimsey, 1994 - this volume) with a total tephra volume of about 20 to 40 x10^6 cubic m (DRE). Tephra plumes rose off the pyroclastic flows to altitudes in excess of 10 km (Woods and Kienle, 1994 - this volume) and were carried mainly northward and eastward by prevailing winds.
Miller and Chouet (1994) also summarize "The volumes of individual domes ranged from 1 to 30x10^6 cubic m and magma supply rates ranged from 1.8 to 2.5 x10^6 cubic m per day. Total dome volume is estimated at about 90x10^6 cubic m (Miller, 1994 - this volume [Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1994, v. 62]).
Miller (1994) estimates total bulk volume of the eruption as 0.1 - 0.2 cubic km.
"These initial explosive events were just the first of 23 major explosive events between December 1989 and April 1990. Following the mid-December explosive phases, the crater vent emitted only minor ash and steam for the next 5-7 days. From December 22 to January 2, 1990, however, a large, over-steepened lava dome grew over the vent. At 5:48 pm on January 2, the first of two powerful explosions destroyed most of the dome and sent ash plumes to over 12 km. Massive block and ash avalanches down the Drift Glacier generated the largest debris flow of the eruption, completely covering the 2-km-wide valley floor and spilling into Cook Inlet. Flood waters entered the oil terminal, as much as 75 cm deep in some buildings, and caused a temporary halt in operations.
"Three eruptions occurred in the next two weeks during which time the vent remained open. The January 8 event occurred with no precursory warnings and the resulting ashfall on the Kenai Peninsula disrupted commerce and transportation. Open-vent eruptions on January 11 and 16 resulted in minor debris flows down the Drift River.
"After the January 16 eruption, another period of dome growth ensued through mid-February. This dome was smaller than the earlier dome but larger than succeeding domes (Miller, 1994). Early on February 15, the dome was destroyed in an explosive eruption that again sent a large debris flow down the Drift River and blanketed the lower Kenai Peninsula with ash. A pyroclastic flow and surge traveled down the canyon, across the piedmont lobe of Drift Glacier, and swept up the opposite valley wall 700 m topping the ridge (Gardner and others, 1994). Flow down the Drift River was largely diverted into a side drainage that carried flood waters close to oil storage tanks at the downstream oil terminal prompting reinforcement of the containment dikes surrounding the tank farm. A new dome began growing immediately following the eruption.
"On February 21, the new, but considerably smaller, dome was destroyed, marking the beginning of a new trend in eruptive behavior. Characteristically, small domes were emplaced and subsequently destroyed explosively or by gravitational collapse, resulting in debris avalanches down the now ice-free canyon leading down to the Drift River valley, and flooding down the Drift River. Ten such eruptions followed from February 24 to April 21 at 4 to 8 day intervals.
"Following the April 21 eruption, growth of the present lava dome began and continued through early June. During the next several months, seismic activity declined dramatically and only steam emissions and minor rock falls from the dome were recorded as the eruption came to an end.
"The 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt seriously affected the populace, commerce, and oil production throughout the Cook Inlet region and air traffic as far away as Texas. Total estimated economic costs are $160 million (Tuck and others, 1992), making this eruption of Redoubt the second most costly in U.S. history."
From Miller and Chouet (1994): "The eruption produced about 20 significant tephra deposits between December 14 and April 26 (Scott and McGimsey, 1994 - this volume) with a total tephra volume of about 20 to 40 x10^6 cubic m (DRE). Tephra plumes rose off the pyroclastic flows to altitudes in excess of 10 km (Woods and Kienle, 1994 - this volume) and were carried mainly northward and eastward by prevailing winds.
Miller and Chouet (1994) also summarize "The volumes of individual domes ranged from 1 to 30x10^6 cubic m and magma supply rates ranged from 1.8 to 2.5 x10^6 cubic m per day. Total dome volume is estimated at about 90x10^6 cubic m (Miller, 1994 - this volume [Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1994, v. 62]).
Miller (1994) estimates total bulk volume of the eruption as 0.1 - 0.2 cubic km.
Impact: From Waythomas and others (1998): "About 23 individual volcanic bursts caused by explosions, dome collapse, or both, occurred during the 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt Volcano. During some of these bursts, vertical clouds or plumes of fine volcanic ash were forcibly expelled into the atmosphere. Ash plumes reached altitudes of 7,000 to more than 12,000 meters above sea level before being dispersed by the prevailing winds. These ash clouds initially drifted to the northeast and east, but eventually moved to the southeast over Canada and into the airspace over the conterminous United States. At least one ash cloud from Redoubt Volcano reached as far west as Texas and the Gulf of Mexico (Casadevall, 1994). Throughout the eruption, clouds of volcanic ash remained a serious threat to aircraft downwind from the volcano and at least seven commercial jet aircraft encountered ash clouds from Redoubt Volcano.
"Volcanic ash from the 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt Volcano is composed of sand-sized and smaller particles of angular pumice, volcanic glass, crystals, and rock fragments. Volcanic ash clouds from Redoubt Volcano occupied a portion of the airspace utilized by jet aircraft and traveled at altitudes ranging from about 4,500 to 12,000 meters (Casadevall, 1994). The ash may interfere with aircraft engine operation and electronic components and its abrasive quality often causes damage to the exterior of jet aircraft, especially the leading edges of wings and cockpit windshields (Casadevall, 1994).
"* * * In addition to the incidents described above, volcanic ash clouds from Redoubt Volcano curtailed activity at two other Anchorage area airports, Merrill Field and Elmendorf Air Force Base. Although no significant amount of ash fallout occurred, ash clouds in the airspace over the Anchorage area and beyond caused numerous flight cancellations, delays, and route changes. During December 1989, more than 90 military cargo flights were diverted from Elmendorf Air Force Base and about 45 flights by military turboprop aircraft were cancelled (Casadevall, 1994). As a result of the 1989-90 eruption, lost revenue at Anchorage International Airport was about $2.6 million (Casadevall, 1994)."
"* * * Ashfall from the 1989-90 eruptions was a serious public health concern for parts of south-central Alaska, especially the Kenai Peninsula. During periods of continuous ash fallout, the public was advised to remain indoors and wear dust masks. Many schools were closed, and some individuals experienced respiratory problems. The municipal airport at Kenai was closed for several days as a result of ash fallout from the January 8, 1990 eruption. Gas-powered turbines at the Beluga power plant, the primary power supply for Anchorage, were shut down in anticipation of the adverse effects of a thick ashfall on February 24, 1990. Only one of the turbines remained in operation for a brief period during the ashfall, but fortunately there were no interruptions in power service."
" * * * During the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, hot pyroclastic flows melted significant parts of the Drift Glacier and the winter snowpack. Some of the ensuing lahars, lahar-runout flows, and floods completely inundated the Drift River valley, threatened the Drift River Oil Terminal, and eventually flowed into Cook Inlet about 35 kilometers downstream from the volcano. At least six lahars in the Drift River reached Cook Inlet during the 1989-90 eruptions (Dorava and Meyer, 1994). The largest of these occurred on January 2, 1990 and inundated Rust Slough, including parts of the Drift River Oil Terminal. At the oil terminal, muddy sediment about 1 meter thick was deposited by this lahar. As the 1989-90 eruptions progressed, additional sediment was delivered to the lower Drift River, Rust Slough, and Cannery Creek by lahars and lahar-runout flows. This caused the braided channel of the Drift River to change its course repeatedly, temporarily increasing the discharge of tributary streams and accelerating erosion. As a result of this process, increased flow in Montana Bill Creek initiated bank erosion that exposed, but did not rupture, a buried oil pipeline that crosses Montana Bill Creek north of the oil terminal (Dorava and Meyer, 1994).
"The 1989-90 eruption began in December at a time when the amount of snow and ice on the volcano was significantly greater than it would be in March and April. Thus, the initial lahars were greater than those that formed later in the eruption. As the eruption progressed, Drift Glacier became deeply scoured and lesser amounts of snow and ice were available for melting by the hot pyroclastic flows, even though some of those flows were larger but less hot than those that were generated earlier in the eruption. As the amount of snow and ice available for scour and entrainment by the pyroclastic flows decreased, so did the size of the resultant lahars.
"* * * During the 1989-90 eruptions, pyroclastic flows were formed primarily by repeated collapse of a lava dome (Gardner and others, 1994). Fourteen distinct lava domes formed over the course of the eruption as viscous lava was slowly extruded (Miller, 1994). As the domes were being extruded, they became oversteepened and then failed by gravitational collapse. The collapse caused a sudden release of pressure from the upper part of the magma chamber which explosively propelled hot gas, water vapor, and rock debris down the slope of the volcano. The resultant pyroclastic flows and associated ash clouds were directed down the east side of Drift Glacier and the Drift River valley, traveling about 8 kilometers downstream from the volcano.
"The pyroclastic flows generated by the 1989-90 eruptions melted and scoured large portions of Drift Glacier. Because the glacier was heavily crevassed and steep, the hot pyroclastic flows incised ice canyons through the glacier, some as large as 40 meters deep and 30 meters wide. This led to the development of lahars downstream from Drift Glacier as meltwater mixed with debris deposited at the distal end of Drift Glacier by the pyroclastic flows.
"During the February 15, 1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, a pyroclastic surge climbed a ridge 700 meters above the terminus of Drift Glacier and about 10 kilometers from the dome, charring woody vegetation, melting cables to seismic monitoring equipment, and partially burning a ptarmigan."
Tuck and Huskey (1992) estimate the total economic cost of the 1989-90 eruptions to be $159,687,070. [60] [1] [44] [61] [62] [45] [46] [16] [28] [19] [63] [64] [65] [54] [66] [67] [68] [69] [70] [71] [55] [40] [51] [72] [49] [73] [41] [3] [5] [6] [8]
Aircraft Impact: From Casadevall (1994): "The December 1989-June 1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano affected commercial and military air operations in the vicinity of Anchorage, Alaska. These effects were due to the direct impact of volcanic ash on jet aircraft, as well as to the rerouting and cancellations of flight operations owing to eruptive activity. Between December and February, five commercial jetliners were damaged from ash encounters. The most serious incident took place on December 15, 1989, when a Boeing 747-400 aircraft temporarily lost power of all four engines after encountering an ash cloud as the airplane descended for a landing in Anchorage. While there were no injuries to passengers, the damage to engines, avionics, and aircraft structure from this encounter is estimated at $80 million. Four additional encounters between jet aircraft and Redoubt ash clouds occurred in the Anchorage area on December 15 and 16, 1989, and February 21, 1990; none resulted in engine failure. Two additional encounters took place on December 17, 1989 when jet airliners encountered the Redoubt cloud over west Texas. At the time of these encounters, the cloud was up to 55 hours old and had traveled in excess of 2,900 nautical miles (5,300 km).
"Following the December 15 encounters, Anchorage International Airport remained open, however, most airline companies cancelled operations for up to several days. As communications between Federal agencies and airlines improved, and as a better understanding of the nature and behavior of ash-rich eruption clouds was achieved, most airlines resumed normal service by early January 1990. The resulting loss of revenue at Anchorage International Airport during several months following the eruption is estimated to total $2.6 million. The impact on general aviation and military operations consisted mostly of cancellation and rerouting of flights. * * * Kenai airport, located on the Kenai peninsula, 43 nautical miles (80 km) east of Redoubt volcano, was shut down by ash fall from the eruption of January 8 and remained closed for several days."
At Elmendorf AFB "* * * Jet fighter operations were limited on December 15-16 and 12 sorties were canceled. During December, about 90 military cargo flights were diverted to either Fairbanks or the Air National Guard base at Anchorage International Airport (AIA). Approximately 45 flights by military turboprop aircraft were canceled in December 1989 due to volcanic activity." [44] [45] [61] [62] [1] [46] [64] [65] [54] [68] [69] [70] [71] [55] [40] [51] [72] [49] [73] [41] [3]
Other Impacts: From Tuck and Huskey (1992): "The Kenai Peninsula governmental sector lost at least 1,010 days of labor due to closures. Schools closed for three days. These were losses that were not made up for 300 non-teaching personnel. The cities of Soldotna and Homer also sent workers home for periods of time during the eruptions. This accounted for about eighty worker days. Finally the Peninsula Hospital let its non-essential workers go for one-half of one day for a loss of 30 worker days (Johnson, Whelan, Haggerty, and Swarner, personal communications). * * * There were numerous power outages caused by volcanic ash during this period." [55] [54] [40] [1]
Images
References Cited
[1] The eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska, December 14, 1989-August 31, 1990, 1990
Brantley, S. R., (ed.), 1990, The eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska, December 14, 1989-August 31, 1990: U.S. Geological Survey Circular C 1061, 33 p., available at http://www.dggs.dnr.state.ak.us/pubs/pubs?reqtype=citation&ID=13450 .[2] Volcanoes of the world [2nd edition], 1994
Simkin, Tom, and Siebert, Lee, 1994, Volcanoes of the world [2nd edition]: Tucson, Arizona, Geoscience Press, 349 p.[3] Redoubt, 1989
Smithsonian Institution, 1989, Redoubt: Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin v. 14, n. 11, unpaged.[4] Redoubt, 1989
Smithsonian Institution, 1989, Redoubt: Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin v. 14, n. 12, unpaged.[5] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 01, unpaged.[6] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 02, unpaged.[7] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 03, unpaged.[8] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 04, unpaged.[9] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 05, unpaged.[10] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 06, unpaged.[11] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 07, unpaged.[12] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 10, unpaged.[13] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 11, unpaged.[14] Photographs of the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1996
Roach, A. L., Neal, C. A., and McGimsey, R. G., 1996, Photographs of the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 96-689, 30 p.[15] Volcanoes of the United States, 1997
Brantley, S. R., 1997, Volcanoes of the United States: The Earth Scientist, v. 14, n. 4, p. 3-13.[16] Hydrologic hazards in the lower Drift River Basin associated with the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Dorava, J. M., and Meyer, D. F., 1994, Hydrologic hazards in the lower Drift River Basin associated with the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 387-407.[17] Proximal pyroclastic deposits from the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska - stratigraphy, distribution, and physical characteristics, 1994
Gardner, C. A., Neal, C. A., Waitt, R. B., and Janda, R. J., 1994, Proximal pyroclastic deposits from the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska - stratigraphy, distribution, and physical characteristics: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 213-250.[18] Catalog of the historically active volcanoes of Alaska, 1998
Miller, T. P., McGimsey, R. G., Richter, D. H., Riehle, J. R., Nye, C. J., Yount, M. E., and Dumoulin, J. A., 1998, Catalog of the historically active volcanoes of Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 98-0582, 104 p.[19] Disruption of Drift glacier and origin of floods during the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Trabant, D. C., Waitt, R. B., and Major, J. J., 1994, Disruption of Drift glacier and origin of floods during the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 369-385.[20] Volcano sends new plume 40,000 feet, 1989
Associated Press, 1989, Volcano sends new plume 40,000 feet: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. December 15-16, 1989, Fairbanks, Alaska, p. 1, 6.[21] Volcanic activity in Alaska: Summary of events and response of the Alaska Volcano Observatory 1992, 1995
McGimsey, R. G., Neal, C. A., and Doukas, M. P., 1995, Volcanic activity in Alaska: Summary of events and response of the Alaska Volcano Observatory 1992: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-83, 26 p.[22] Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 12, unpaged.[23] Seismological aspects of the 1989-1990 eruption at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: the Materials Failure Forecast Method (FFM) with RSAM and SSAM seismic data, 1994
Cornelius, R. R., and Voight, Barry, 1994, Seismological aspects of the 1989-1990 eruption at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: the Materials Failure Forecast Method (FFM) with RSAM and SSAM seismic data: in Miller, T. P., (ed.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 469-498.[24] 10 years of volcanic activity in Alaska: 1983 to 1992: a video, 1995
Doukas, M. P., McGimsey, R. G., and Dorava, J. M., 1995, 10 years of volcanic activity in Alaska: 1983 to 1992: a video: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-61-B, 12 p.[25] 10 years of volcanic activity in Alaska: 1983-1992: A video (Pyre Peak, Akutan, Bogoslof, Westdahl, Veniaminof, Augustine, Redoubt, and Spurr volcanoes), 1995
Doukas, M. P., McGimsey, R. G., and Dorava, J. M., 1995, 10 years of volcanic activity in Alaska: 1983-1992: A video (Pyre Peak, Akutan, Bogoslof, Westdahl, Veniaminof, Augustine, Redoubt, and Spurr volcanoes): U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-0061-A, Anchorage, AK, KAKM Video, 1 videocassette.[26] Redoubt, 1993
Miller, T. P., 1993, Redoubt: in Annual report of the world volcanic eruptions in 1990, Bulletin of Volcanic Eruptions, v. 30, p. 66-70.[27] Dome growth and destruction during the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, 1994
Miller, T. P., 1994, Dome growth and destruction during the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geophysical Research, v. 62, p. 197-212.[28] The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt volcano: an introduction, 1994
Miller, T. P., and Chouet, B. A., 1994, The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt volcano: an introduction: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 1-10.[29] The dynamics and thermodynamics of volcanic clouds: theory and observations from the April 15 and April 21, 1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Woods, A. W., and Kienle, Juergen, 1994, The dynamics and thermodynamics of volcanic clouds: theory and observations from the April 15 and April 21, 1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 273-299.[30] Redoubt volcano, southern Alaska: a hazard assessment based on eruptive activity through 1968, 1993
Till, A. B., Yount, M. E., and Riehle, J. R., 1993, Redoubt volcano, southern Alaska: a hazard assessment based on eruptive activity through 1968: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1996, 19 p., 1 sheet, scale 1:125,000.[31] Statistical forecasting of repetitious dome failures during the waning eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, February-April 1990, 1994
Page, R. A., Lahr, J. C., Chouet, B. A., Power, J. A., and Stephens, C. D., 1994, Statistical forecasting of repetitious dome failures during the waning eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, February-April 1990: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 183-196.[32] An experiment to detect and locate lightning associated with eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, 1994
Hoblitt, R. P., 1994, An experiment to detect and locate lightning associated with eruptions of Redoubt Volcano: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 499-517.[33] Postglacial eruption history of Redoubt volcano, Alaska, 1994
Beget, J. E., and Nye, C. J., 1994, Postglacial eruption history of Redoubt volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 31-54.[34] Hydrologic hazards at recently active volcanoes in the Cook Inlet Region, Alaska, 1995
Dorava, J. M., and Waythomas, C. F., 1995, Hydrologic hazards at recently active volcanoes in the Cook Inlet Region, Alaska: in Herrman, R., (ed.), Annual summer symposium -- 1995, Water resources and environmental hazards: emphasis on hydrologic and cultural insight in the Pacific Rim, Honolulu, HI, American Water Resources Association, p. 91-98.[35] Redoubt volcano and the Alaska Volcano Observatory, 10 years later, 2001
McGimsey, G., 2001, Redoubt volcano and the Alaska Volcano Observatory, 10 years later: in Gough, L. P. and Wilson, F. H., (eds.), Geological studies in Alaska by the U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper PP 1633, p. 5-12.[36] Volcanoes of the Wrangell Mountains and Cook Inlet Region, Alaska-selected photographs, 1996
Neal, Christina, and McGimsey, Robert, 1996, Volcanoes of the Wrangell Mountains and Cook Inlet Region, Alaska-selected photographs: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS 0039, 1 CD-ROM.[37] Fire & ice, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Fire & ice: University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute Quarterly 8, p. 4-5.[38] The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, 1990
Alaska Volcano Observatory, 1990, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Eos, v. 71, n. 7, p. 265, 266, 272-273, 275.[39] The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, 1990
Alaska Volcano Observatory, 1990, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: On the Rim…Geography NOW in the Northern World, Supplement to Alaska Geographic, v. 17, n. 2, p. 86-87.[40] The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: the eruption and its hazards, 1990
Alaska Volcano Observatory, 1990, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: the eruption and its hazards: Eos, v. 71, n. 7, p. 265, 272-273, 275.[41] Volcanic ash dusts interior; Airline flights on hold, 1989
Associated Press, 1989, Volcanic ash dusts interior; Airline flights on hold: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. December 17, 1989, Fairbanks, Alaska, p. 1.[42] Redoubt blows, 1991
Brantley, S. R., 1991, Redoubt blows: in Rennick, Penny, (ed.), Alaska's Volcanoes, Alaska Geographic, v. 18, n. 2, p. 35-37.[43] Volcanoes of the United States, 1999
Brantley, S. R., 1999, Volcanoes of the United States: U.S. Geological Survey General Interest Publication 44 p.[44] Volcanic hazards and aviation safety: lessons of the past decade, 1992
Casadevall, T. J., 1992, Volcanic hazards and aviation safety: lessons of the past decade: Federal Aviation Administration Aviation Safety Journal, v. 2, p. 3-11.[45] The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: impacts on aircraft operations, 1994
Casadevall, T. J., 1994, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: impacts on aircraft operations: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 301-316.[46] An aircraft encounter with a Redoubt ash cloud (a satellite view), 1994
Dean, K. G., Whiting, L., and Jiao, H., 1994, An aircraft encounter with a Redoubt ash cloud (a satellite view): in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 333-339.[47] Satellite analyses of movement and characteristics of the Redoubt Volcano plume, January 8, 1990, 1994
Dean, Ken, Bowling, S. A., Shaw, Glenn, and Tanaka, Hiroshi, 1994, Satellite analyses of movement and characteristics of the Redoubt Volcano plume, January 8, 1990: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 339-352.[48] Redoubt, 1992
Kienle, J., Miller, T. P., and Reeder, J. W., 1992, Redoubt: in (eds.), Annual report of the world volcanic eruptions in 1989, Bulletin of Volcanic Eruptions, v. 29, p. 73-76.[49] Volcanic ash and aircraft operations, 1994
Miller, E., 1994, Volcanic ash and aircraft operations: in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: Proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 203-206.[50] A perilous passage through volcanic ash, 1989
Monastersky, R., 1989, A perilous passage through volcanic ash: Science News, v. 136, n. 27, p. 407.[51] Volcanic ash - Danger to aircraft in the North Pacific, 1997
Neal, C. A., Casadevall, T. J., Miller, T. P., Hendley, J. W. II., and Stauffer, P. H., 1997, Volcanic ash - Danger to aircraft in the North Pacific: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet FS 30-0097, 2 p.[52] Satellite measurement of sulfur dioxide from the Redoubt eruptions of 1989-1990, 1994
Schnetzler, C. C., Doiron, S. D., Walter, L. S., and Krueger, A. J., 1994, Satellite measurement of sulfur dioxide from the Redoubt eruptions of 1989-1990: in Miller, T. P., (ed.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 353-357.[53] Character, mass, distribution, and origin of tephra-fall deposits of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, south-central Alaska, 1994
Scott, W. E., and McGimsey, R. G., 1994, Character, mass, distribution, and origin of tephra-fall deposits of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, south-central Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 251-272.[54] The economic consequences of the 1989-90 Mt. Redoubt eruptions, 1992
Tuck, B. H., and Huskey, Lee, 1992, The economic consequences of the 1989-90 Mt. Redoubt eruptions: University of Alaska Anchorage, Institute of Social and Economic Research unpublished report Anchorage, AK, variously paginated.[55] Economic disruptions by Redoubt volcano: assessment methodology and anecdotal empirical evidence, 1994
Tuck, B. H., and Huskey, Lee, 1994, Economic disruptions by Redoubt volcano: assessment methodology and anecdotal empirical evidence: in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 137-140.[56] Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part II, Evidence from mineral and glass chemistry, 1994
Swanson, S. E., Nye, C. J., Miller, T. P., and Avery, V. F., 1994, Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part II, Evidence from mineral and glass chemistry: in Miller, T. P., (ed.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 453-468.[57] Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part I. Whole-rock major- and trace-element chemistry, 1994
Nye, C. J., Swanson, S. E., Avery, V. F., and Miller, T. P., 1994, Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part I. Whole-rock major- and trace-element chemistry: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 429-452.[58] Breeze blows ash around Kenai area, 1990
Associated Press, 1990, Breeze blows ash around Kenai area: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. 88, n. 90, Fairbanks, Alaska, p. 3.[59] Redoubt blows its top, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Redoubt blows its top: Time, v. 135, n. 3, p. 33.[60] Preliminary volcano-hazard assessment for Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1997
Waythomas, C. F., Dorava, J. M., Miller, T. P., Neal, C. A., and McGimsey, R. G., 1997, Preliminary volcano-hazard assessment for Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 97-857, 40 p., 1 plate, scale unknown.[61] Latest Mt. Redoubt eruptions force several airlines to cancel night flights in Anchorage, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Latest Mt. Redoubt eruptions force several airlines to cancel night flights in Anchorage: Aviation Week and Space Technology, v. 132, n. 3, p. 23.[62] New eruptions from Mt. Redoubt disrupt Alaskan air traffic again, 1990
Unknown, 1990, New eruptions from Mt. Redoubt disrupt Alaskan air traffic again: Aviation Week and Space Technology, v. 132, n. 2, p. 53.[63] Flood generation and destruction of "Drift" Glacier by the 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1992
Trabant, D. C., and Meyer, D. F., 1992, Flood generation and destruction of "Drift" Glacier by the 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: Annals of Glaciology, v. 16, p. 33-38.[64] Alaska's Redoubt volcano affects airport, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Alaska's Redoubt volcano affects airport: Alaska Economic Report, n. December 28, p. 3.[65] Alaska volcano plays havoc with airliners, 1989
Tobin, C., 1989, Alaska volcano plays havoc with airliners: Whitehorse Star, n. December 18, p. 1.[66] Alaska's Redoubt volcano shuts down oil wells, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Alaska's Redoubt volcano shuts down oil wells: Alaska Economic Report, n. January 15, p. 7.[67] Volcano stops Alaska crude re Redoubt, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Volcano stops Alaska crude re Redoubt: Whitehorse Star, n. January 19, p. 5.[68] Volcano leaves its mark on Alaska travel, schools re Redoubt, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Volcano leaves its mark on Alaska travel, schools re Redoubt: Northland News, v. 6, n. 2, p. 7.[69] Alaska's Redoubt volcano disrupts holiday travel, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Alaska's Redoubt volcano disrupts holiday travel: All-Alaska Weekly, n. December 22, p. 1.[70] Re Redoubt volcano - coughing volcano fouls up Alaska air, mail schedules, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Re Redoubt volcano - coughing volcano fouls up Alaska air, mail schedules: Whitehorse Star, n. December 19, p. 5.[71] Volcano halts flights, mail within Alaska, Redoubt takes break, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Volcano halts flights, mail within Alaska, Redoubt takes break: Tundra Times, n. December 25, p. 1.[72] Volcanic ash cloud shuts down all four engines of a Boeing 747-400, causes $80 million in damage, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Volcanic ash cloud shuts down all four engines of a Boeing 747-400, causes $80 million in damage: Aviation week and Space Technology, v. 132, p. 93.[73] Volcanic ash - a rain of terra, 1990
Steenblik, J. W., 1990, Volcanic ash - a rain of terra: Airline Pilot, v. June/July, p. 9-15.Complete Eruption References
Physical, psychological and behavioural responses of aircraft occupants to volcanic emissions, 2025
Horwell, C.J., Ravenhall, S., Clarkson, R., Edmonds, M., Rubin, G.J., Witham, C., and Howell, R., 2025, Physical, psychological and behavioural responses of aircraft occupants to volcanic emissions: Journal of Applied Volcanology v. 14, 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13617-025-00153-4
Towards scientific forecasting of magmatic eruptions, 2024
Acocella, V., Ripepe, M., Rivalta, E., Peltier, A., Galetto, F., and Joseph, E., 2024, Towards scientific forecasting of magmatic eruptions, Nature Reviews Earth & Environment v. 5, p. 5-22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-023-00492-z
Role of source, mineralogy, and organic complexation on lability and Fe isotopic composition of terrestrial Fe sources to the Gulf of Alaska, 2024
Huang, L., Aarons, S.M., Koffman, B.G., Cheng, W., Hanschka, L., Munk, L.A., Jenckes, J., Norris, E., and Arendt, C.A., 2024, Role of source, mineralogy, and organic complexation on lability and Fe isotopic composition of terrestrial Fe sources to the Gulf of Alaska: ACS Earth and Space Chemistry v. 8, no. 8, p. 1505-1518. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.3c00338
Volcanoes of the world: an illustrated catalog of Holocene volcanoes and their eruptions, 2003
Siebert, L., and Simkin, T., 2002-, Volcanoes of the world: an illustrated catalog of Holocene volcanoes and their eruptions: Smithsonian Institution, Global Volcanism Program Digital Information Series GVP-3, http://volcano.si.edu/search_volcano.cfm, unpaged internet resource.
Evolution of the December 14, 1989 precursory long-period event swarm at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 2001
Stephens, C. D., and Chouet, B. A., 2001, Evolution of the December 14, 1989 precursory long-period event swarm at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 109, n. 1, p. 133-148.
Volcanoes of the United States, 1999
Brantley, S. R., 1999, Volcanoes of the United States: U.S. Geological Survey General Interest Publication 44 p.

Catalog of the historically active volcanoes of Alaska, 1998
Miller, T. P., McGimsey, R. G., Richter, D. H., Riehle, J. R., Nye, C. J., Yount, M. E., and Dumoulin, J. A., 1998, Catalog of the historically active volcanoes of Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 98-0582, 104 p.

Volcanic ash - Danger to aircraft in the North Pacific, 1997
Neal, C. A., Casadevall, T. J., Miller, T. P., Hendley, J. W. II., and Stauffer, P. H., 1997, Volcanic ash - Danger to aircraft in the North Pacific: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet FS 30-0097, 2 p.

Preliminary volcano-hazard assessment for Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1997
Waythomas, C. F., Dorava, J. M., Miller, T. P., Neal, C. A., and McGimsey, R. G., 1997, Preliminary volcano-hazard assessment for Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 97-857, 40 p., 1 plate, scale unknown.

Syneruptive mixing, degassing, and crystallization at Redoubt Volcano, eruption of December, 1989 to May 1990, 1997
Wolf, K. J., and Eichelberger, J. C., 1997, Syneruptive mixing, degassing, and crystallization at Redoubt Volcano, eruption of December, 1989 to May 1990: Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 75, n. 1-2, p. 19-38.

Volcanoes of the Wrangell Mountains and Cook Inlet Region, Alaska-selected photographs, 1996
Neal, Christina, and McGimsey, Robert, 1996, Volcanoes of the Wrangell Mountains and Cook Inlet Region, Alaska-selected photographs: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS 0039, 1 CD-ROM.

Photographs of the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1996
Roach, A. L., Neal, C. A., and McGimsey, R. G., 1996, Photographs of the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 96-689, 30 p.
Hydrologic hazards at recently active volcanoes in the Cook Inlet Region, Alaska, 1995
Dorava, J. M., and Waythomas, C. F., 1995, Hydrologic hazards at recently active volcanoes in the Cook Inlet Region, Alaska: in Herrman, R., (ed.), Annual summer symposium -- 1995, Water resources and environmental hazards: emphasis on hydrologic and cultural insight in the Pacific Rim, Honolulu, HI, American Water Resources Association, p. 91-98.

A compilation of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide emission-rate data from Cook Inlet volcanoes (Redoubt, Spurr, Iliamna, and Augustine), Alaska during the period from 1990 to 1994, 1995
Doukas, M. P., 1995, A compilation of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide emission-rate data from Cook Inlet volcanoes (Redoubt, Spurr, Iliamna, and Augustine), Alaska during the period from 1990 to 1994: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-0055, 15 p.
10 years of volcanic activity in Alaska: 1983-1992: A video (Pyre Peak, Akutan, Bogoslof, Westdahl, Veniaminof, Augustine, Redoubt, and Spurr volcanoes), 1995
Doukas, M. P., McGimsey, R. G., and Dorava, J. M., 1995, 10 years of volcanic activity in Alaska: 1983-1992: A video (Pyre Peak, Akutan, Bogoslof, Westdahl, Veniaminof, Augustine, Redoubt, and Spurr volcanoes): U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-0061-A, Anchorage, AK, KAKM Video, 1 videocassette.
Volcanic activity in Alaska: Summary of events and response of the Alaska Volcano Observatory 1992, 1995
McGimsey, R. G., Neal, C. A., and Doukas, M. P., 1995, Volcanic activity in Alaska: Summary of events and response of the Alaska Volcano Observatory 1992: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-83, 26 p.
Magmatic behavior during the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1995
Wolf, K. J., 1995, Magmatic behavior during the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: University of Alaska Fairbanks unpublished M.S. thesis, 188 p.

Silicic volcanism: ascent of viscous magmas from crustal reservoirs, 1995
Eichelberger, J.C., 1995. Silicic volcanism: ascent of viscous magmas from crustal reservoirs. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, v. 23, no. 1, p. 41-63.
Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part I. Whole-rock major- and trace-element chemistry, 1994
Nye, C. J., Swanson, S. E., Avery, V. F., and Miller, T. P., 1994, Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part I. Whole-rock major- and trace-element chemistry: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 429-452.

Postglacial eruption history of Redoubt volcano, Alaska, 1994
Beget, J. E., and Nye, C. J., 1994, Postglacial eruption history of Redoubt volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 31-54.

The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: impacts on aircraft operations, 1994
Casadevall, T. J., 1994, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: impacts on aircraft operations: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 301-316.

Emission rates of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide from Redoubt Volcano, Alaska during the 1989-1990 eruptions, 1994
Casadevall, T. J., Doukas, M. P., Neal, C. A., McGimsey, R. G., and Gardner, C. A., 1994, Emission rates of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide from Redoubt Volcano, Alaska during the 1989-1990 eruptions: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 519-530.

Precursory swarms of long-period events at Redoubt volcano (1989-1990), Alaska: their origin and use as a forecasting tool, 1994
Chouet, B. A., Page, R. A., Stephens, C. D., Lahr, J. C., and Power, J. A., 1994, Precursory swarms of long-period events at Redoubt volcano (1989-1990), Alaska: their origin and use as a forecasting tool: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 95-135.

Seismological aspects of the 1989-1990 eruption at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: the Materials Failure Forecast Method (FFM) with RSAM and SSAM seismic data, 1994
Cornelius, R. R., and Voight, Barry, 1994, Seismological aspects of the 1989-1990 eruption at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: the Materials Failure Forecast Method (FFM) with RSAM and SSAM seismic data: in Miller, T. P., (ed.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 469-498.

An aircraft encounter with a Redoubt ash cloud (a satellite view), 1994
Dean, K. G., Whiting, L., and Jiao, H., 1994, An aircraft encounter with a Redoubt ash cloud (a satellite view): in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 333-339.

Satellite analyses of movement and characteristics of the Redoubt Volcano plume, January 8, 1990, 1994
Dean, Ken, Bowling, S. A., Shaw, Glenn, and Tanaka, Hiroshi, 1994, Satellite analyses of movement and characteristics of the Redoubt Volcano plume, January 8, 1990: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 339-352.

Hydrologic hazards in the lower Drift River Basin associated with the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Dorava, J. M., and Meyer, D. F., 1994, Hydrologic hazards in the lower Drift River Basin associated with the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 387-407.

Influence of volcanic ash clouds on gas turbine engines, 1994
Dunn, M. G., and Wade, D. P., 1994, Influence of volcanic ash clouds on gas turbine engines: in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: Proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 107-117.
Proximal pyroclastic deposits from the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska - stratigraphy, distribution, and physical characteristics, 1994
Gardner, C. A., Neal, C. A., Waitt, R. B., and Janda, R. J., 1994, Proximal pyroclastic deposits from the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska - stratigraphy, distribution, and physical characteristics: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 213-250.

Volcanic ash and aircraft operations, 1994
Miller, E., 1994, Volcanic ash and aircraft operations: in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: Proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 203-206.
Dome growth and destruction during the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, 1994
Miller, T. P., 1994, Dome growth and destruction during the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geophysical Research, v. 62, p. 197-212.

The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt volcano: an introduction, 1994
Miller, T. P., and Chouet, B. A., 1994, The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt volcano: an introduction: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 1-10.

Seismic evolution of the 1989-1990 eruption sequence of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Power, J. A., Lahr, J. C., Page, R. A., Chouet, B. A., Stephens, C. D., Harlow, D. H., Murray, T. L., and Davies, J. N., 1994, Seismic evolution of the 1989-1990 eruption sequence of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 69-94.

Observations of the 1989-90 Redoubt Volcano eruption clouds using AVHRR satellite imagery, 1994
Schneider, D. J., and Rose, W. I., 1994, Observations of the 1989-90 Redoubt Volcano eruption clouds using AVHRR satellite imagery: in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 405-418.

Satellite measurement of sulfur dioxide from the Redoubt eruptions of 1989-1990, 1994
Schnetzler, C. C., Doiron, S. D., Walter, L. S., and Krueger, A. J., 1994, Satellite measurement of sulfur dioxide from the Redoubt eruptions of 1989-1990: in Miller, T. P., (ed.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 353-357.

Character, mass, distribution, and origin of tephra-fall deposits of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, south-central Alaska, 1994
Scott, W. E., and McGimsey, R. G., 1994, Character, mass, distribution, and origin of tephra-fall deposits of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt volcano, south-central Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 251-272.

Volcanoes of the world [2nd edition], 1994
Simkin, Tom, and Siebert, Lee, 1994, Volcanoes of the world [2nd edition]: Tucson, Arizona, Geoscience Press, 349 p.
Seismological aspects of the 1989-1990 eruptions at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: The SSAM perspective, 1994
Stephens, C. D., Chouet, B. A., Page, R. A., Lahr, J. C., and Power, J. A., 1994, Seismological aspects of the 1989-1990 eruptions at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: The SSAM perspective: Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 153-182.

Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part II, Evidence from mineral and glass chemistry, 1994
Swanson, S. E., Nye, C. J., Miller, T. P., and Avery, V. F., 1994, Geochemistry of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Part II, Evidence from mineral and glass chemistry: in Miller, T. P., (ed.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 453-468.

Disruption of Drift glacier and origin of floods during the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Trabant, D. C., Waitt, R. B., and Major, J. J., 1994, Disruption of Drift glacier and origin of floods during the 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 369-385.

Economic disruptions by Redoubt volcano: assessment methodology and anecdotal empirical evidence, 1994
Tuck, B. H., and Huskey, Lee, 1994, Economic disruptions by Redoubt volcano: assessment methodology and anecdotal empirical evidence: in Casadevall, T. J., (ed.), Volcanic ash and aviation safety: proceedings of the first international symposium on volcanic ash and aviation safety, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2047, p. 137-140.

Mount Redoubt volcano eruption, 1994
University of Alaska Fairbanks, 1994, Mount Redoubt volcano eruption: 1 videocassette.
The dynamics and thermodynamics of volcanic clouds: theory and observations from the April 15 and April 21, 1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Woods, A. W., and Kienle, Juergen, 1994, The dynamics and thermodynamics of volcanic clouds: theory and observations from the April 15 and April 21, 1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 273-299.

Earthquake classification, location, and error analysis in a volcanic environment: implications for the magmatic system of the 1989-1990 eruptions at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Lahr, J. C., Chouet, B. A., Stephens, C. D., Power, J. A., and Page, R. A., 1994, Earthquake classification, location, and error analysis in a volcanic environment: implications for the magmatic system of the 1989-1990 eruptions at Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 137-151.

Statistical forecasting of repetitious dome failures during the waning eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, February-April 1990, 1994
Page, R. A., Lahr, J. C., Chouet, B. A., Power, J. A., and Stephens, C. D., 1994, Statistical forecasting of repetitious dome failures during the waning eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, February-April 1990: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 183-196.

Vapor saturation and accumulation in magmas of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Gerlach, T. M., Westrich, H. R., Casadevall, T. J., and Finnegan, D. L., 1994, Vapor saturation and accumulation in magmas of the 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 317-337.

The influence of Redoubt Volcano emissions on snow chemistry, 1994
Jaffe, D. A., Cerundolo, Bianca, and Kelley, Jennifer, 1994, The influence of Redoubt Volcano emissions on snow chemistry: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 359-367.

Unusual ice diamicts emplaced during the December 15, 1989 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1994
Waitt, R. B., Neal, C. A., Gardner, C. A., Pierson, T. C., and Major, J. J., 1994, Unusual ice diamicts emplaced during the December 15, 1989 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in Chouet, B. A. and Miller, T. P., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1, p. 409-428.

An experiment to detect and locate lightning associated with eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, 1994
Hoblitt, R. P., 1994, An experiment to detect and locate lightning associated with eruptions of Redoubt Volcano: in Miller, T. P. and Chouet, B. A., (eds.), The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 62, n. 1-4, p. 499-517.

The 1989–1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano: an introduction, 1994
Miller, T.P. and Chouet, B.A., 1994. The 1989-1990 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano: an introduction: Journal of Volcanology and geothermal research, v. 62, no. 1-4, p. 1-10.
Redoubt, 1993
Miller, T. P., 1993, Redoubt: in Annual report of the world volcanic eruptions in 1990, Bulletin of Volcanic Eruptions, v. 30, p. 66-70.
Redoubt volcano, southern Alaska: a hazard assessment based on eruptive activity through 1968, 1993
Till, A. B., Yount, M. E., and Riehle, J. R., 1993, Redoubt volcano, southern Alaska: a hazard assessment based on eruptive activity through 1968: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1996, 19 p., 1 sheet, scale 1:125,000.
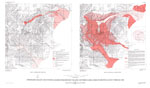
Volcanic hazards and aviation safety: lessons of the past decade, 1992
Casadevall, T. J., 1992, Volcanic hazards and aviation safety: lessons of the past decade: Federal Aviation Administration Aviation Safety Journal, v. 2, p. 3-11.

Geomorphic response to the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1992
Dorava, J. M., 1992, Geomorphic response to the 1989-90 eruptions of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: in American Water Resources Association, Annual meeting -- 1992, n. 114, Fairbanks, AK, 1992, Alaska Section, Bethesda, MD, American Water Resources Association, p. 87-88.
Redoubt, 1992
Kienle, J., Miller, T. P., and Reeder, J. W., 1992, Redoubt: in (eds.), Annual report of the world volcanic eruptions in 1989, Bulletin of Volcanic Eruptions, v. 29, p. 73-76.
Flood generation and destruction of "Drift" Glacier by the 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska, 1992
Trabant, D. C., and Meyer, D. F., 1992, Flood generation and destruction of "Drift" Glacier by the 1989-90 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska: Annals of Glaciology, v. 16, p. 33-38.
NOAA satellite helps aviators avoid ash from Alaskan volcano, 1992
Unknown, 1992, NOAA satellite helps aviators avoid ash from Alaskan volcano: Aviation Week and Space Technology, v. 137, n. 1, p. 31.
USGS volcano hazards program saved lives, 1991
Bush, S., 1991, USGS volcano hazards program saved lives: Eos, v. 72, n. 30, p. 314.
The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, 1990
Alaska Volcano Observatory, 1990, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: Eos, v. 71, n. 7, p. 265, 266, 272-273, 275.

The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: the eruption and its hazards, 1990
Alaska Volcano Observatory, 1990, The 1989-1990 eruption of Redoubt Volcano: the eruption and its hazards: Eos, v. 71, n. 7, p. 265, 272-273, 275.
Breeze blows ash around Kenai area, 1990
Associated Press, 1990, Breeze blows ash around Kenai area: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. 88, n. 90, Fairbanks, Alaska, p. 3.
The eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska, December 14, 1989-August 31, 1990, 1990
Brantley, S. R., (ed.), 1990, The eruption of Redoubt volcano, Alaska, December 14, 1989-August 31, 1990: U.S. Geological Survey Circular C 1061, 33 p., available at http://www.dggs.dnr.state.ak.us/pubs/pubs?reqtype=citation&ID=13450 .
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 01, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 02, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 03, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 04, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 05, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 06, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 07, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 10, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 11, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1990
Smithsonian Institution, 1990, Redoubt: Global Volcanism Network Bulletin v. 15, n. 12, unpaged.
Redoubt Volcano, Cook Inlet, Alaska: a hazard assessment based on eruptive activity through 1968, 1990
Till, A. B., Yount, Elizabeth, and Riehle, J. R., 1990, Redoubt Volcano, Cook Inlet, Alaska: a hazard assessment based on eruptive activity through 1968: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 90-0246, 33 p., 2 plates, scale 1:125,000.
Alaska volcano gushes ash, lava re Mount Redoubt, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Alaska volcano gushes ash, lava re Mount Redoubt: The Tundra Drums, n. January 4, p. 4.
Alaska volcano slumbers but more eruptions possible re Redoubt volcano, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Alaska volcano slumbers but more eruptions possible re Redoubt volcano: Whitehorse Star, n. January 4, p. 5.
Ash and mudflow from Redoubt eruption cause disruption in Alaska, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Ash and mudflow from Redoubt eruption cause disruption in Alaska: Earth in Space, v. 2, n. 7, p. 7-10.
Eruption plume from Redoubt volcano, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Eruption plume from Redoubt volcano: Eos, v. 71, n. 1, p. 4.
Latest Mt. Redoubt eruptions force several airlines to cancel night flights in Anchorage, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Latest Mt. Redoubt eruptions force several airlines to cancel night flights in Anchorage: Aviation Week and Space Technology, v. 132, n. 3, p. 23.
New eruptions from Mt. Redoubt disrupt Alaskan air traffic again, 1990
Unknown, 1990, New eruptions from Mt. Redoubt disrupt Alaskan air traffic again: Aviation Week and Space Technology, v. 132, n. 2, p. 53.
Re Alaska tourism - increasing concern over volcano, Mount Redoubt, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Re Alaska tourism - increasing concern over volcano, Mount Redoubt: Alaska Economic Report, n. January 26, p. 1.
Redoubt blows its top, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Redoubt blows its top: Time, v. 135, n. 3, p. 33.
Redoubt blows top, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Redoubt blows top: Whitehorse Star, n. January 9, p. 5.
Redoubt cuts Mapco earnings, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Redoubt cuts Mapco earnings: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. 88, n. 90, p. 1.
Redoubt eruptions spark volcano watch, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Redoubt eruptions spark volcano watch: University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute Quarterly 8, p. 1, 15-16.
Redoubt volcano ash to be studied by scientific aircraft re Alaska, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Redoubt volcano ash to be studied by scientific aircraft re Alaska: All-Alaska Weekly, n. January 15, p. 17.
The blast not heard around the world, 1990
Unknown, 1990, The blast not heard around the world: National Geographic Magazine, v. 178, n. 6, p. 146.
Volcanic ash cloud shuts down all four engines of a Boeing 747-400, causes $80 million in damage, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Volcanic ash cloud shuts down all four engines of a Boeing 747-400, causes $80 million in damage: Aviation week and Space Technology, v. 132, p. 93.
Volcano leaves its mark on Alaska travel, schools re Redoubt, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Volcano leaves its mark on Alaska travel, schools re Redoubt: Northland News, v. 6, n. 2, p. 7.
Volcano stops Alaska crude re Redoubt, 1990
Unknown, 1990, Volcano stops Alaska crude re Redoubt: Whitehorse Star, n. January 19, p. 5.
Volcanic ash dusts interior; Airline flights on hold, 1989
Associated Press, 1989, Volcanic ash dusts interior; Airline flights on hold: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. December 17, 1989, Fairbanks, Alaska, p. 1.
Volcano sends new plume 40,000 feet, 1989
Associated Press, 1989, Volcano sends new plume 40,000 feet: Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, v. December 15-16, 1989, Fairbanks, Alaska, p. 1, 6.
A perilous passage through volcanic ash, 1989
Monastersky, R., 1989, A perilous passage through volcanic ash: Science News, v. 136, n. 27, p. 407.
Redoubt, 1989
Smithsonian Institution, 1989, Redoubt: Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin v. 14, n. 11, unpaged.
Redoubt, 1989
Smithsonian Institution, 1989, Redoubt: Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin v. 14, n. 12, unpaged.
Drift River: tragedy in the wind?, 1989
Spence, Hal, 1989, Drift River: tragedy in the wind?: Homer News, v. 17, n. 52, Homer, Alaska, p. 1, 14.
Alaska volcano plays havoc with airliners, 1989
Tobin, C., 1989, Alaska volcano plays havoc with airliners: Whitehorse Star, n. December 18, p. 1.
Alaska's Redoubt volcano affects airport, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Alaska's Redoubt volcano affects airport: Alaska Economic Report, n. December 28, p. 3.
Alaska's Redoubt volcano disrupts holiday travel, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Alaska's Redoubt volcano disrupts holiday travel: All-Alaska Weekly, n. December 22, p. 1.
Mount Redoubt starts erupting re Alaska volcano, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Mount Redoubt starts erupting re Alaska volcano: Tundra Times, n. December 18, p. 23.
Re Redoubt volcano - coughing volcano fouls up Alaska air, mail schedules, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Re Redoubt volcano - coughing volcano fouls up Alaska air, mail schedules: Whitehorse Star, n. December 19, p. 5.
Volcano halts flights, mail within Alaska, Redoubt takes break, 1989
Unknown, 1989, Volcano halts flights, mail within Alaska, Redoubt takes break: Tundra Times, n. December 25, p. 1.
Geology of Iniskin-Tuxedni region, Alaska, 1966
Detterman, R. L., and Hartsock, J. K., 1966, Geology of Iniskin-Tuxedni region, Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper PP 0512, 78 p., 6 sheets, scale 1:63,360, 1:96,000, 1:1,000,000.
