References
Mallalieu, J., Barr, I.D., Spagnolo, M., Mullan, D.J., Symeonakis, E., Edwards, B.R., and Martin, M.D., 2024, Proximity to active volcanoes enhances glacier velocity: Communications Earth & Environment v. 5, 679. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-024-01826-5
Alaska Volcano Observatory, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Weather Service, Federal Aviation Administration, Department of Defense, United States Coast Guard, Division of Homeland Security and Emergency Management, Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation, and Alaska Department of Health and Social Services (participating agencies), 2022, Alaska interagency operating plan for volcanic ash episodes, 85 p.
Cameron, C.E., Crass, S.W., and AVO Staff, eds, 2022, Geologic database of information on volcanoes in Alaska (GeoDIVA): Alaska Division of Geologic and Geophysical Surveys Digital Data Series 20, https://doi.org/10.14509/geodiva, https://doi.org/10.14509/30901.
Power, J.A., Haney, M.M., Botnick, S.M., Dixon, J.P., Fee, David, Kaufman, A.M., Ketner, D.M., Lyons, J.J., Parker, Tom, Paskievitch, J.F., Read, C.W., Searcy, Cheryl, Stihler, S.D., Tepp, Gabrielle, and Wech, A.G., 2020, Goals and development of the Alaska Volcano Observatory seismic network and application to forecasting and detecting volcanic eruptions: Seismological Research Letters, doi: 10.1785/0220190216 .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler S.D., Haney, M.M., Lyons, J.J., Ketner, D.M., Mulliken, K.M., Parker, T., and Power, J.A., 2019, Catalog of earthquake parameters and description of seismograph and infrasound stations at Alaskan volcanoes - January 1, 2013, through December 31, 2017: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 1115, 92 p., https://doi.org/10.3133/ds1115.
Power, J.A., Friberg, P.A., Haney, M.M., Parker, T., Stihler, S.D., and Dixon, J.P., 2019, A unified catalog of earthquake hypocenters and magnitudes at volcanoes in Alaska—1989 to 2018: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2019–5037, 17 p., https://doi.org/10.3133/sir20195037.
Cameron, C.E., and Snedigar, S.F., 2016, Alaska Volcano Observatory image database: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Digital Data Series 13, https://www.avo.alaska.edu/images/. https://doi.org/10.14509/29689.
Cameron, C.E., and Nye, C.J., 2014, Preliminary database of Quaternary vents in Alaska: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Miscellaneous Publication 153, 11 p., doi:10.14509/27357 .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D, Power, J.A., Haney, Matt, Parker, Tom, Searcy, C.K., and Prejean, Stephanie, 2013, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2012: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 789, 84 p., available at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/789/ .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D., Power, J.A., and Searcy, C.K., 2012, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2011: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 730, 82 p., available online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/730/pdf/ds730.pdf .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D., Power, J.A., and Searcy, C.K., 2011, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2010: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 645, 82 p., available online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/645/
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D., Power, J.A., and Searcy, C.K., 2010, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2009: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 531, 84 p., available online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/531/ .
Dixon, J.P., and Stihler, S.D., 2009, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2008: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 467, 88 p., available at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/467/ .
Mastin, L.G., Guffanti, Marianne, Ewert, J.E., and Spiegel, Jessica, 2009, Preliminary spreadsheet of eruption source parameters for volcanoes of the world: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2009-1133, v. 1.2, 25 p., available at http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2009/1133/ .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D., Power, J.A., and Searcy, Cheryl, 2008, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2006: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 326, 79 p., available at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/326/ .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D. and Power, J.A., 2008, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2007: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 367, 82 p., available online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/367/ .
Ewert, John, 2007, System for ranking relative threats of U.S. volcanoes: Natural Hazards Review, v. 8, n. 4, p. 112-124.
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D., Power, J.A., Tytgat, Guy, Estes, Steve, and McNutt, S.R., 2006, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2005: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2006-1264, 78 p., available at http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2006/1264/ .
Dixon, J.P., Stihler, S.D., Power, J.A., Tytgat, Guy, Estes, Steve, Prejean, Stephanie, Sanchez, J.J., Sanches, Rebecca, McNutt, S.R., and Paskievitch, John, 2005, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2004: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2005-1312, 74 p., available online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2005/1312/.
Dixon, J. P., Stihler, S. D., Power, J. A., Tytgat, Guy, Moran, S. C., Sanchez, J. J., McNutt, S. R., Estes, Steve, and Paskievitch, John, 2004, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2003: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2004-1234, 69 p.
Brantley, S. R., McGimsey, R. G., and Neal, C. A., 2004, The Alaska Volcano Observatory - Expanded monitoring of volcanoes yields results: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet FS 2004-3084, 2 p.
Siebert, L., and Simkin, T., 2002-, Volcanoes of the world: an illustrated catalog of Holocene volcanoes and their eruptions: Smithsonian Institution, Global Volcanism Program Digital Information Series GVP-3, http://volcano.si.edu/search_volcano.cfm, unpaged internet resource.
Cameron, C. E., Triplehorn, J. H., and Robar, C. L., 2003, Bibliography of information on Alaska volcanoes: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Miscellaneous Publication MP 131, 1 CD-ROM.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Dixon, J. P., Stihler, S. D., Power, J. A., Tytgat, Guy, Moran, S. C., Sanchez, John, Estes, Steve, McNutt, S. R., and Paskievitch, John, 2003, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1 through December 31, 2002: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 03-0267, 58 p.
Dixon, J. P., Stihler, S. D., Power, J. A., Tytgat, Guy, Estes, Steve, Moran, S. C., Paskievitch, John, and McNutt, S. R., 2002, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1, 2000 through December 31, 2001: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 02-0342, 56 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Schaefer, Janet, and Nye, C. J., 2002, Historically active volcanoes of the Aleutian Arc: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Miscellaneous Publication MP 0123, unpaged, 1 sheet, scale 1:3,000,000. Superceded by Miscellaneous Publication 133: http://www.dggs.dnr.state.ak.us/pubs/pubs?reqtype=citation&ID=20181
Jolly, A. D., Stihler, S. D., Power, J. A., Lahr, J. C., Paskievitch, John, Tytgat, Guy, Estes, Steve, Lockheart, A. D., Moran, S. C., McNutt, S. R., and Hammond, W. R., 2001, Catalog of earthquake hypocenters at Alaskan volcanoes: January 1, 1994 through December 31, 1999: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 01-0189, 22 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Wallace, K. L., McGimsey, R. G., and Miller, T. P., 2000, Historically active volcanoes in Alaska, a quick reference: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet FS 0118-00, 2 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Sigurdsson, Haraldur, (ed.), 2000, Encyclopedia of volcanoes: San Diego, CA, Academic Press, 1417 p.
Nye, C. J., Queen, Katherine, and McCarthy, A. M., 1998, Volcanoes of Alaska: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Information Circular IC 0038, unpaged, 1 sheet, scale 1:4,000,000, available at http://www.dggs.dnr.state.ak.us/pubs/pubs?reqtype=citation&ID=7043 .
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Miller, T. P., McGimsey, R. G., Richter, D. H., Riehle, J. R., Nye, C. J., Yount, M. E., and Dumoulin, J. A., 1998, Catalog of the historically active volcanoes of Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 98-0582, 104 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Wilson, F. H., Weber, F. R., Dochat, T. M., Miller, T. P., and Detterman, R. L., 1997, Revised geologic map of the Cold Bay and False Pass quadrangles, Alaska Peninsula: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 97-0866, 34 p., 1 sheet, scale 1:250,000.
Neal, Christina, and McGimsey, R. G., 1997, Volcanoes of the Alaska Peninsula and Aleutian Islands selected photographs: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS 0040, 1 CD-ROM.
McGimsey, R. G., and Miller, T. P., 1995, Quick reference to Alaska's active volcanoes and listing of historical eruptions, 1760-1994: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-0520, 13 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 1995, Volcanoes of Alaska: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Information Circular IC 0038, unpaged, 1 sheet, scale 1:4,000,000.
Plafker, George, Moore, J. C., and Winkler, G. R., 1994, Geology of the southern Alaska margin: in Plafker, George and Berg, H. C., (eds.), The Geology of Alaska, Geological Society of America The Geology of North America series v. G-1, p. 389-449.
Simkin, Tom, and Siebert, Lee, 1994, Volcanoes of the world [2nd edition]: Tucson, Arizona, Geoscience Press, 349 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Fournelle, J. H., Marsh, B. D., and Myers, J. D., 1994, Age, character, and significance of Aleutian arc volcanism: in Plafker, George and Berg, H. C., (eds.), The Geology of Alaska, Geological Society of America The Geology of North America Series v. G-1, p. 723-758.
Khlebnikov, K. T., 1994, Notes on Russian America, Parts II-V: Kad'iak, Unalashka, Atkha, the Pribylovs (translated by Marina Ramsay): Liapunova, R. G. and Fedorova, S. G., (comps.), Kingston, Ontario and Fairbanks, Alaska, The Limestone Press, 424 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Miller, T. P., and Richter, D. H., 1994, Quaternary volcanism in the Alaska Peninsula and Wrangell Mountains, Alaska: in Plafker, George, Jones, D. L., and Berg, H. C., (eds.), The Geology of Alaska, Geological Society of America The Geology of North America series v. G-1, p. 759-779.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Bergsland, Knut, comp., 1994, Aleut dictionary, Unangam Tunudgusii, an unabridged lexicon of the Aleutian, Pribilof, and Commander Islands Aleut language: University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska Native Language Center, 739 p.
Motyka, R. J., Liss, S. A., Nye, C. J., and Moorman, M. A., 1993, Geothermal resources of the Aleutian Arc: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Professional Report PR 0114, 17 p., 4 sheets, scale 1:1,000,000.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
March, G. D., 1993, Holocene volcanoes of the Aleutian Arc, Alaska: Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys Public-Data File PDF 93-85, unpaged, 1 sheet, scale 1:2,000,000.
Singer, B. S., O'Neil, J. R., and Brophy, J. G., 1992, Oxygen isotope constraints on the petrogenesis of Aleutian arc magmas: Geology, v. 20, n. 4, p. 367-370.
Wilson, F. H., Miller, T. P., and Detterman, R. L., 1992, Preliminary geologic map of the Cold Bay and False Pass quadrangles, Alaska Peninsula: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 92-0545, 10 p., 1 plate, scale 1:250,000.
Mouginis-Mark, P. J., Rowland, S. K., and Smith, G. A., 1992, ERS-1 radar data for Aleutian and Alaskan volcanoes [abs.]: Eos, v. 73, n. 43, p. 613-614.
Fournelle, John, and Marsh, B. D., 1991, Shishaldin Volcano: Aleutian high-alumina basalts and the question of plagioclase accumulation: Geology, v. 19, n. 3, p. 234-237.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Fournelle, John, 1990, Geology and geochemistry of Fisher Caldera, Unimak Island, Aleutians: initial results [abs.]: Eos, v. 71, n. 43, p. 1698-1699.
Wood, C. A., and Kienle, Juergen, (eds.), 1990, Volcanoes of North America: United States and Canada: New York, Cambridge University Press, 354 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
DuBois, G. D., Wilson, F. H., Detterman, R. L., and Hopkins, R. T., 1989, Reconnaissance geology and exploration geochemistry of King Cove, Alaska Peninsula: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 89-0352, 23 p.
Fournelle, J., and Marsh, B. D., 1989, Geology and petrology of Shishaldin Volcano, Aleutian Arc [abs.]: in International Geological Congress, 28, Abstracts, p. 504-505.
Major, J. J., and Newhall, C. G., 1989, Snow and ice perturbation during historical volcanic eruptions and the formation of lahars and floods: Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 52, p. 1-27.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Fournelle, J. H., 1988, Geology and petrology of Shishaldin volcano, Unimak Island, Aleutian Arc, Alaska: The Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. dissertation, 507 p., 2 plates, scale unknown.
Fournelle, John, and Marsh, B. D., 1987, Shishaldin Volcano, Unimak Island, Aleutians: Unordinary arc lavas II: Significant REE patterns: Eos, v. 68, n. 16, p. 461.
Miller, T. P., and Smith, R. L., 1987, Late Quaternary caldera-forming eruptions in the eastern Aleutian arc, Alaska: Geology, v. 15, n. 5, p. 434-438.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Luedke, R. G., and Smith, R. L., 1986, Map showing distribution, composition, and age of Late Cenozoic volcanic centers in Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Miscellaneous Investigations Series Map I 1091-F, unpaged, 3 sheets, scale 1:1,000,000.
Marsh, B. D., 1982, The Aleutians: in Thorpe, R. S., (ed.), Andesites: orogenic andesites and related rocks, Chichester, United Kingdom, John Wiley & Sons, p. 99-114.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Simkin, Tom, Siebert, Lee, McClelland, Lindsay, Bridge, David, Newhall, Christopher, and Latter, J. H., 1981, Volcanoes of the world: Stroudsburg, PA, Hutchinson Publishing Company, 233 p.
Motyka, R. J., and Moorman, M. A., 1981, Reconnaissance of thermal spring sites in the Aleutian Arc, Atka Island to Becharof Lake: in Geothermal Resources Council Transactions, v. 5, p. 111-114.
Hudson, Travis, 1979, Calc-alkaline plutonism along the Pacific rim of southern Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 79-0953, 31 p.
Smith, R. L., Shaw, H. R., Luedke, R. G., and Russell, S. L., 1978, Comprehensive tables giving physical data and thermal energy estimates for young igneous systems of the United States: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 78-0925, p. 1-25.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
McLean, H., Engelhardt, C. L., and Howell, D. G., 1978, Reconnaissance geologic map of the Cold Bay and False Pass quadrangles, Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 78-0323, unpaged, 1 plate.
Arctic Environmental Information and Data Center, 1978, Aleutian/Pribilof Islands region community profiles: unpaged.
White, D. E., and Williams, D. L., 1975, Assessment of geothermal resources of the United States - 1975: U.S. Geological Survey Circular C 0726, 155 p.
Veniaminov, Ivan, 1968, Notes on the islands of the Unalashka district; and, Notes on the Atkhan Aleuts and the Kolosh [translated from Russian by Richard Henry Geogheghan]: Martin, Fredericka, (ed.), Unpublished manuscript, Fairbanks, AK, 944 p.
Waring, G. A., 1965, Thermal springs of the United States and other countries of the world - a summary: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper PP 0492, 383 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Waldron, H. H., 1961, Geologic reconnaissance of Frosty Peak volcano and vicinity, Alaska: in Investigations of Alaskan volcanoes, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1028-T, p. 677-708, 1 plate, scale 1:250,000.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Powers, H. A., 1958, Alaska Peninsula-Aleutian Islands: in Williams, H., (ed.), Landscapes of Alaska, Los Angeles, CA, University of California Press, p. 61-75.
Coats, R. R., 1950, Volcanic activity in the Aleutian Arc: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 0974-B, p. 35-49, 1 sheet, scale 1:5,000,000.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Coats, R. R., 1947, Reconnaissance geology of some western Aleutian Islands: U.S. Geological Survey Alaskan Volcano Investigations Report 0002, p. 95-105.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
U.S. Department of Commerce, and Coast and Geodetic Survey, 1947, United States coast pilot, Alaska Part 2, Yakutat Bay to Arctic Ocean: Washington DC, United States Government Printing Office, 659 p.
Denton, G. H., 1945, Glaciers of the Aleutian Islands: in Field, W. O., (ed.), Mountain glaciers of the Northern Hemisphere, v. 2, Hanover, NH, Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, p. 641-650.
Hrdlicka, Ales, 1945, The Aleutian and Commander Islands and their inhabitants: Philadelphia, PA, Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology, 630 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Hubbard, B. R., 1935, Cradle of the storms: New York, Dodd, Mead, 285 p.
Finch, R. H., 1934, Shishaldin volcano: in Pacific Science Congress, 5, Proceedings, v. 3, Victoria and Vancouver, BC, 1933, p. 2369-2376.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Jaggar, T. A., 1928, Alaskan notes: The Volcano Letter, v. 162, p. 1.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Dall, W. H., 1918, Reminiscences of Alaskan volcanoes: Scientific Monthly, v. 7, n. 1, p. 80-90.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Sapper, Karl, 1917, Katalog der geschichtlichen vulkanausbruche: Strassburg, Germany, Karl J. Trubner, 358 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Dunn, Robert, 1906, An island rises from the sea to annex itself: The Washington Post, Washington, D.C., October 14, 1906, p. 44.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Westdahl, F., 1903, Mountains on Unimak Island, Alaska: National Geographic Magazine, v. 14, n. 3, p. 91-99.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Stanley-Brown, J.., 1899, Shishaldin as a field for exploration: National Geographic Magazine, v. 10, n. 8, p. 281-288.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Plummer, F. G., 1898, Reported volcanic eruptions in Alaska, Puget Sound, etc., 1690-1896: in Holden, E. S., (ed.), A Catalogue of Earthquakes on the Pacific Coast 1769-1897, Smithsonian Institution Miscellaneous Collections 1087, City of Washington D.C., Smithsonian Institution, p. 24-27.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
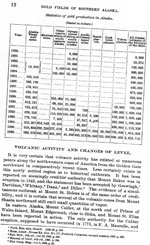
Becker, G. F., 1898, Reconnaissance of the gold fields of southern Alaska with some notes on general geology: U.S. Geological Survey Annual Report 0018, p. 1-86, 6 sheets, scale unknown.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Grewingk, Constantine, 1850, Grewingk's geology of Alaska and the Northwest Coast of America [edited by Marvin W. Falk, translation by Fritz Jaensch published 2003]: Rasmuson Library Historical Translation Series 11, Fairbanks, AK, The University of Alaska Press, 242 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC shelf
Veniaminov, Ivan, 1840, Notes on the islands of the Unalaska district [translated from Russian by Lydia T. Black and R.H. Geoghegan in 1984]: Pierce, R. A., (ed.), Kingston, Ontario, Limestone Press, 511 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet
Veniaminov, I., 1840, Notes on the islands of the Unalashka district [Zapiski ob ostravakh Unalashkinskogo otdela]: v. 1-3, St. Petersburg, Russiisko-Amerikanskoi Kompanii, unknown.
Sauer, Martin, 1802, Expedition to the northern parts of Russia, for ascertaining the degree of latitude and longitude of the mouth of the river Kovima; of the whole coast of the Tshutski, to East Cape; and of the islands in the eastern ocean, stretching to the American coast: London, A. Strahan, 3332 p.
Coats, R. R., Past volcanic activity in the Aleutian arc: U.S. Geological Survey Volcano Investigations Report 1, 18 p.
Hard Copy held by AVO at FBKS - CEC file cabinet